
Zimbabwe (Template:PronEng), officially the Republic of Zimbabwe, and formerly Southern Rhodesia, the Republic of Rhodesia and Zimbabwe Rhodesia, is a landlocked country in the southern part of the continent of Africa, between the Zambezi and Limpopo rivers. It is bordered by South Africa to the south, Botswana to the southwest, Zambia to the northwest, and Mozambique to the east. The official language of Zimbabwe is English. However, the majority of the population speaks Shona, which is the native language of the Shona people, a Bantu Language; the other native language of Zimbabwe being Sindebele, which is spoken by the Matabele people.
From circa 1250–1629, the area that is known as Zimbabwe today was ruled under the Mutapa Empire, also known as Mwene Mutapa, Monomotapa or the Empire of Great Zimbabwe, which was renowned for its gold trade routes with Arabs. However, Portuguese settlers destroyed the trade and began a series of wars which left the empire in near collapse in the early 17th century. In 1834, the Ndebele people arrived while fleeing from the Zulu leader Shaka, making the area their new empire, Matabeleland. In the 1880s, the British arrived with Cecil Rhodes's British South Africa Company. In 1898, the name Southern Rhodesia was adopted.
As colonial rule was ending throughout the continent, and as African-majority governments assumed control in neighbouring Northern Rhodesia and in Nyasaland, the white-minority Rhodesia government led by Ian Smith made a Unilateral Declaration of Independence (UDI) from the United Kingdom on 11 November 1965. The United Kingdom deemed this an act of rebellion, but did not re-establish control by force. The white-minority government declared itself a "republic" in 1970. It was not recognised by the UK or any other state. A civil war ensued, with Joshua Nkomo's ZAPU and Robert Mugabe's ZANU using assistance from the governments of Zambia and Mozambique.
On 18 April 1980, the country attained recognised independence and along with it a new name, Zimbabwe, new flag, and government led by Robert Mugabe of ZANU. Canaan Banana served as the first president with Mugabe as prime minister. In 1987, the government amended the constitution to provide for an executive president and abolished the office of prime minister. The constitutional changes went into effect on 1 January 1988, establishing Robert Mugabe as president.
Under the leadership of Mugabe, land issues, which the liberation movement promised to solve, re-emerged as the vital issue in the 1990s. Beginning in 2000, Mugabe began an effort to redistribute land from white holders (predominantly large farms) to 250,000 Africans.
Zimbabwe is currently experiencing a hard currency shortage, which has led to hyperinflation and chronic shortages in imported fuel and consumer goods. Mugabe's critics blame his programme of land reform. However, Mugabe claims that massive financial isolation through American, British and EU legislation such as the Zimbabwe Democracy and Economic Recovery Act (ZDERA) of 2001 is the actual cause of hyperinflation. Under ZDERA, the United States is prohibited from supporting any efforts by the International Monetary Fund and other financial institutions to extend loans, credit or debt cancellation to the government of Zimbabwe. As Zimbabwe needs to import all its energy, and oil is paid for in US dollars, this made the country vulnerable to financial sanctions like ZDERA.Template:Fact
Zimbabwe's current economic and food crisis, described by some observers as the country's worst humanitarian crisis since independence, has been attributed, in varying degrees, to government economic mismanagement, government prohibitions on relief efforts from foreign NGOs (non-governmental organizations), a drought affecting the entire region, and the HIV/AIDS epidemic.[1]
Zimbabwe[]
Zimbabwe first participated at the Olympic Games under that name in 1980, and has sent athletes to compete in every Summer Olympic Games since then. Previously, Rhodesia had participated in the Games on three occasions since 1928. The nation has never participated in the Winter Olympic Games.
Zimbabwean athletes have won a total of four medals: the surprise gold medal by the Zimbabwe women's national field hockey team in 1980, and Kirsty Coventry's three medals in swimming at the 2004 Summer Olympics.
The National Olympic Committee for Zimbabwe was created in 1934 and recognized by the International Olympic Committee in 1980.
Medal tables[]
Template:See also
Medals by Games[]
| 1980 Moscow | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1984 Los Angeles | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1988 Seoul | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1992 Barcelona | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1996 Atlanta | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2000 Sydney | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2004 Athens | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| Total | 2 | 1 | 1 | 4 |
|---|
Medals by sport[]
| Swimming | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| Field hockey | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Total | 2 | 1 | 1 | 4 |
|---|
Etymology[]
The name Zimbabwe derives from "Dzimba dza mabwe" meaning "great stone house" in the Shona language.[2] Its use as the country's name is a tribute to Great Zimbabwe, site of the capital of the Empire of Great Zimbabwe. In other languages, such as German, the initial Z is replaced with an S so as to produce the same sound in the phonics of the said language; for example Zimbabwe is spelled "Simbabwe".[3]
History[]
- Main article: History of Zimbabwe
Pre-colonial era[]
Stone Age hunters, related to today's Khoisan people, occupied the area about 5000 years ago or earlier. They depicted scenes of life in rock paintings across Zimbabwe; these are known as the Bushman paintings.[4] Iron Age Bantu-speaking peoples began migrating into the area around AD 300, eventually displacing the earlier hunters. These included the ancestors of the Shona, who account for roughly four-fifths of the country's population today.[5][6]

The Great Zimbabwe ruins in Masvingo.
By the Middle Ages, there was a Bantu civilization in the region, as evidenced by ruins at Great Zimbabwe and other smaller sites, whose outstanding achievement is a unique dry stone architecture. Around the early 10th century, trade developed with Phoenicians on the Indian Ocean coast, helping to develop Great Zimbabwe in the 11th century. The state traded gold, ivory, and copper for cloth and glass. It ceased to be the leading Shona state in the mid-15th century. In 1837-8, the Shona were conquered by the Ndebele, who arrived from south of the Limpopo and forced them to pay tribute and concentrate in northern Zimbabwe.[7]
Colonial era (1888–1965)[]
- Main article: Southern Rhodesia
Matabeleland in the 1800s.
In 1888, British colonialist Cecil Rhodes obtained a concession for mining rights from King Lobengula of the Ndebele peoples.[8] Cecil Rhodes presented this concession to persuade the government of the United Kingdom to grant a royal charter to his British South Africa Company (BSAC) over Matabeleland, and its subject states such as Mashonaland. Permission was sought by Rhodes to negotiate similar concessions covering all territory between the Limpopo River and Lake Tanganyika, then known as 'Zambesia'. In accordance with the terms of aforementioned concessions and treaties, [9] Cecil Rhodes promoted the colonisation of the region's land, and British hegemony over labour, precious metals and other mineral resources.[10] In 1895 the BSAC adopted the name 'Rhodesia' for the territory of Zambesia, in honor of Cecil Rhodes. In 1898 'Southern Rhodesia' became the official denotation for the region south of the Zambezi,[11] which later became Zimbabwe. The region to the north was administered separately by the BSAC and later named Northern Rhodesia, now Zambia.
The Shona staged unsuccessful revolts (known as Chimurenga) against encroachment upon their lands, by clients of BSAC and Cecil Rhodes in 1896 and 1897.[12] Following the failed insurrections of 1896-97 the Ndebele and Shona groups became subject to Rhodes's administration thus precipitating European settlement en masse which led to land distribution disproportionately favouring Europeans, displacing the Shona, Ndebele, and other indigenous peoples.
Southern Rhodesia became a self-governing British colony in October 1923, subsequent to a 1922 referendum. Rhodesians served on behalf of the United Kingdom during World War II, mainly in the East African Campaign against Axis forces in Italian East Africa.
In 1953, in the face of African opposition,[13] Britain consolidated the two colonies of Rhodesia with Nyasaland (now Malawi) in the ill-fated Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland which was dominated by Southern Rhodesia. Growing African nationalism and general dissent, particularly in Nyasaland, admonished Britain to dissolve the Union in 1963, forming three colonies. On November 11, 1965, the prime minister of Southern Rhodesia Ian Smith unilaterally declared independence from the United Kingdom. Although Smith's declaration was not recognized by the United Kingdom nor any other significant power, Southern Rhodesia dropped the designation 'Southern', and claimed nation status as the Republic of Rhodesia in 1970.[14][15]
UDI and civil war (1965–1979)[]
- Main article: Rhodesia
Ian Smith signing the Unilateral Declaration of Independence on November 11, 1965 with his cabinet watching.
After the Unilateral Declaration of Independence (UDI), the British government requested United Nations economic sanctions against Rhodesia as negotiations with the Smith administration in 1966 and 1968 ended in stalemate. The Smith administration declared itself a republic in 1970 which was recognised only by South Africa,[16][17] then governed by its apartheid administration. Over the years, the guerrilla fighting against Smith's UDI government intensified. As a result, the Smith government opened negotiations with the leaders of the Patriotic Fronts—Zimbabwe African National Union (ZANU) and the Zimbabwe African People's Union (ZAPU). ZANU was led by Robert Mugabe and ZAPU was led by Joshua Nkomo.
In March 1978, with his regime near the brink of collapse, Smith signed an accord with three black leaders, led by Bishop Abel Muzorewa, who offered safeguards for white civilians. As a result of the Internal Settlement, elections were held in April 1979. The United African National Council (UANC) party won a majority in this election. On June 1 1979, the leader of UANC, Abel Muzorewa, became the country's prime minister and the country's name was changed to Zimbabwe Rhodesia. The internal settlement left control of the country's police, security forces, civil service, and judiciary in white hands. It assured whites of about one-third of the seats in parliament. It was essentially a power-sharing arrangement which did not amount to majority rule.[18] However, on June 12, the United States Senate voted to end economic sanctions against Zimbabwe Rhodesia.
Following the Commonwealth Heads of Government Meeting (CHOGM) held in Lusaka from 1-7 August 1979, the British government invited Muzorewa and the leaders of the Patriotic Front to participate in a constitutional conference at Lancaster House. The purpose of the conference was to discuss and reach agreement on the terms of an independence constitution, and that elections should be supervised under British authority to enable Rhodesia to proceed to legal independence and the parties to settle their differences by political means. Lord Carrington, Secretary of State for Foreign and Commonwealth Affairs of the United Kingdom, chaired the conference.[19] The conference took place from 10 September–15 December 1979 with 47 plenary sessions. On December 1, 1979, delegations from the British and Rhodesian governments and the Patriotic Front signed the Lancaster House Agreement, ending the civil war.[20]
Independence (1980)[]
- Main article: Lancaster House Agreement
President Canaan Banana (right) and prime minister Robert Mugabe attend the ceremony for the independence of Zimbabwe on April 18, 1980
Britain's Lord Soames was appointed governor to oversee the disarming of revolutionary guerrillas, the holding of elections and the granting of independence to an uneasy coalition government with Joshua Nkomo, head of ZAPU. In the free elections of February 1980, Mugabe and his ZANU won a landslide victory.[21] Mugabe won the re-election.
In 1982, Joshua Nkomo was ousted from his cabinet, sparking fighting between ZAPU supporters in the Ndebele-speaking region of the country and the ruling ZANU. A peace accord was negotiated in 1987, resulting in ZAPU's merger (1988) into the ZANU-PF.
Decline[]
Land issues, which the liberation movement had promised to solve, re-emerged as the vital issue for the ruling party beginning in 1999. Despite majority rule and the existence of a "willing-buyer-willing-seller" land reform programme since the 1980s, ZANU (PF) claimed that whites made up less than 1% of the population but held 70% of the country's commercially viable arable land (though these figures are disputed by many outside the Government of ZimbabweTemplate:Fact). Mugabe began to redistribute land to blacks in 2000 with a compulsory land redistribution. Charges that the programme as a whole is designed to reward loyal Mugabe deputies have persisted in Zimbabwe since the beginning of the process.
The legality and constitutionality of the process has regularly been challenged in the Zimbabwean High and Supreme Courts; however, the policing agencies have rarely acted in accordance with court rulings on these matters. The chaotic implementation of the land reform led to a sharp decline in agricultural exports, traditionally the country's leading export producing sector.[22] Mining and tourism have surpassed agriculture. As a result, Zimbabwe is experiencing a severe hard-currency shortage, which has led to hyperinflation and chronic shortages in imported fuel and consumer goods. In 2002, Zimbabwe was suspended from the Commonwealth of Nations on charges of human rights abuses during the land redistribution and of election tampering .[23]
Following elections in 2005, the government initiated "Operation Murambatsvina", a purported effort to crack down on illegal markets and homes that had seen slums emerge in towns and cities. This action has been widely condemned by opposition and international figures, who charge that it has left a substantial section of urban poor homeless. The Zimbabwe government has described the operation as an attempt to provide decent housing to the population although they have yet to deliver any new housing for the forcibly removed people.[24].
Zimbabwe's current economic and food crisis, described by some observers as the country's worst humanitarian crisis since independence, has been attributed in varying degrees, to a drought affecting the entire region, the HIV/AIDS epidemic, and the government's price controls and land reforms.[25]
Life expectancy at birth for males in Zimbabwe has dramatically declined since 1990 from 60 to 37, the lowest in the world. Life expectancy for females is even lower at 34 years.[26] Concurrently, the infant mortality rate has climbed from 53 to 81 deaths per 1,000 live births in the same period. Currently, 1.8 million Zimbabweans live with HIV.
On March 29, 2008, Zimbabwe held a presidential election along with a parliamentary election, The three major candidates were Robert Mugabe of the Zimbabwe African National Union - Patriotic Front (ZANU-PF), Morgan Tsvangirai of the Movement for Democratic Change (MDC), and Simba Makoni, an independent. The results of this election were withheld for several weeks, following which it was generally acknowledged that the MDC had achieved a significant majority of seats. The presidential election is the subject of a separate article.
Geography[]
- Main article: Geography of Zimbabwe
Template:MapLibrary
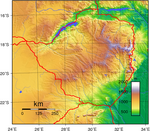
Topography of Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe is a landlocked country, surrounded by South Africa to the south, Botswana to the west, Zambia to the northwest and Mozambique to the east and northeast. Zimbabwe also meets Namibia to the west at a single point. To the south, Zimbabwe is separated from South Africa by the Limpopo River. The north-western border is defined by the Zambezi River. Zimbabwe's highest peak is Mount Nyangani (formerly Mount Inyangani), at 2,592 m (8,504 ft);[27] it lies within the Nyanga National Park in the east of the country. The lowest point of Zimbabwe is the junction of the Runde and Save rivers at 162 m (531 ft). Victoria Falls is a popular tourist destination on the Zambezi.
Zimbabwe's climate is largely tropical, however this is moderated by altitude. It has a short rainy season which lasts about four months between November and March. The terrain of Zimbabwe is mostly high plateau with higher central plateau (high veld) and a mountainous range in the east.
Natural hazards in Zimbabwe include recurring droughts and unpredictable rainfall, though severe storms are rare. There are several environmental issues in Zimbabwe including deforestation, soil erosion, land degradation, air pollution and water pollution. The black rhinoceros herd—once the largest concentration of the species in the world—has fallen significantly.[28] Poor mining practices have led to toxic waste and heavy metal pollution. Some of these problems have been worsened by the current political crisis, whereby Zimbabweans are cutting down forests for firewood or for sale.[29]
Administrative divisions[]
- Main article: Provinces of Zimbabwe

Administrative divisions of Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe is divided into eight provinces and two cities with provincial status.[29] These are territorial divisions for the purposes of administrative, political and geographical demarcation. The provinces are subdivided into 59 districts and 1,200 municipalities. Zimbabwe's provinces are Bulawayo (city), Harare (city), Manicaland, Mashonaland Central, Mashonaland East, Mashonaland West, Masvingo, Matabeleland North, Matabeleland South, and Midlands. The names of the provinces are generally generated from the Mashonaland and Matabeleland divide which existed before colonisation. These two lands were the tribal homes of the Shona people and the Matabele people. The provinces have regional capitals and these are generally, on the whole, in the centre of the province but not always the largest town/city in the province.[30]
Government and politics[]
- Main article: Politics of Zimbabwe
Robert Mugabe heading to the opening of Parliament
Zimbabwe has a parliamentary government. Under constitutional changes in 2005, an upper chamber, the Senate, was reinstated.[31] The House of Assembly is the lower chamber of Parliament.
President Robert Mugabe's Zimbabwe African National Union – Patriotic Front has been the dominant political party in Zimbabwe since independence.[32] In 1987 then-prime minister Mugabe revised the constitution and made himself president. His ZANU party has won every election since independence. In particular, the elections of 1990 were nationally and internationally condemned as being rigged, with the second-placed party, Edgar Tekere's Zimbabwe Unity Movement, winning only 16% of the vote.[33] Presidential elections were again held in 2002 amid allegations of vote-rigging, intimidation and fraud.[34] General elections were held in Zimbabwe on 30 March 2008.[35] The official results required a runoff between Mugabe and Morgan Tsvangirai, the opposition leader, however the MDC challenged these results, claiming widespread election fraud by the Mugabe government. The runoff was scheduled for June 27, 2008. On June 22nd, however, citing the continuing unfairness of the process and refusing to participate in a "violent, illegitimate sham of an election process", Tsvangirai pulled out of the presidential run-off, effectively handing victory to Mugabe.[36]
The Movement for Democratic Change led by Morgan Tsvangirai is the largest opposition party. The MDC was formerly split into two factions. One faction, led by Arthur Mutambara contested the elections to the Senate, while the other, led by Morgan Tsvangirai, opposed to contesting the elections, stating that participation in a rigged election is tantamount to endorsing Mugabe's claim that past elections were free and fair. However, the opposition parties have resumed participation in national and local elections as recently as 2006. The two MDC camps had their congresses in 2005 with Morgan Tsvangirai being elected to lead the main splinter group which has become more popular than the other group. Mutambara, a robotics professor and former NASA robotics specialist has replaced Welshman Ncube who was the interim leader after the split. Morgan Tsvangirai did not participate in the Senate elections, while the Mutambara faction participated and won five seats in the senate. The Mutambara faction has however been weakened by defections from MPs and individuals who are disillusioned by their manifesto. As of 2008, the Tsvangirai-led MDC has become the most popular, with crowds as large as 20,000 attending their rallies as compared to between 500–5,000 for the other splinter group.[37] There is wide disagreement in Zimbabwe and neighbouring states as to whether a divided MDC can win presidential elections against a disciplined ruling party. The opposition continues to be weak in rural areas, where a large number of the population of Zimbabwe resides. On 28 April 2008, Tsvangirai and Mutambara announced at a joint news conference in Johannesburg that the two MDC factions were reuniting, enabling the MDC to have a clear parliamentary majority.[38][39] Tsvangirai said that Mugabe could not remain President without a parliamentary majority.[39] On the same day, Silaigwana announced that the recounts for the final five constituencies had been completed, that the results were being collated and that they would be published on 29 April.[40]
The 2005 Zimbabwe parliamentary elections were held on March 31 and multiple claims of vote rigging, election fraud and intimidation were made by the MDC and Jonathan Moyo, calling for investigations into 32 of the 120 constituencies.[41] Jonathan Moyo participated in the elections despite the allegations and won a seat as an independent member of Parliament.
Human rights[]
- Main article: Human rights in Zimbabwe

Protesters against the Mugabe regime abroad; protests are discouraged by Zimbabwean police in Zimbabwe
There are widespread reports of systematic and escalating violations of human rights in Zimbabwe under the Mugabe administration and his party, ZANU-PF.
According to human rights organisations such as Amnesty International[42] and Human Rights Watch[43] the government of Zimbabwe violates the rights to shelter, food, freedom of movement and residence, freedom of assembly and the protection of the law. There are assaults on the media, the political opposition, civil society activists, and human rights defenders.
Opposition gatherings are frequently the subject of brutal attacks by the police force, such as the crackdown on a March 11, 2007 Movement for Democratic Change (MDC) rally. In the events, party leader Morgan Tsvangirai and 49 other opposition activists were arrested and severely beaten by the police. After his release, Morgan Tsvangirai told the BBC that he suffered head injuries and blows to the arms, knees and back, and that he lost a significant amount of blood.[44] The police action was strongly condemned by the UN Secretary-General, Ban Ki-moon, the European Union and the United States.[44] While noting that the activists had suffered injuries, but not mentioning the cause of them,[45] the Zimbabwean government-controlled daily newspaper The Herald claimed the police had intervened after demonstrators "ran amok looting shops, destroying property, mugging civilians, and assaulting police officers and innocent members of the public". The newspaper also argued that the opposition had been "wilfully violating the ban on political rallies".[45]
The ZBC is the public broadcaster
There is also an abuse of human rights in the media. The Zimbabwean government suppresses freedom of the press and freedom of speech.[42] It has also been repeatedly accused of using the public broadcaster, the Zimbabwe Broadcasting Corporation, as a propaganda tool.[46] Newspapers critical of the government, such as the Daily News, closed after bombs exploded at their offices and the government refused to renew their license.[47][48] BBC News, Sky News, CNN and Al Jazeera have also been banned from filming or reporting from Zimbabwe. They continue to report on happenings within Zimbabwe from neighbouring countries like South Africa.[49] [50]
Military[]
- Main article: Military of Zimbabwe

Flag of the Zimbabwe Defence Forces
The existence of the Zimbabwe Defence Forces (ZDF) is enshrined in the Constitution of Zimbabwe, Chapter X, 96 (1), which states that, Template:Cquote
The ZDF was set up by the integration of three belligerent forces, the Zimbabwe African National Liberation Army, (ZANLA) and the Zimbabwe People's Revolutionary Army, (ZIPRA) on one side and the Rhodesian Security Forces (RSF) on the other at the end of the Liberation Struggle in 1980. The Integration period saw the formation of The Zimbabwe National Army (ZNA) and Air Force of Zimbabwe (AFZ) as separate entities under the command of Rtd General Solomon Mujuru and the late Rtd Air Chief Marshal Josiah Tungamirai respectively. The integration commanders handed over the Zimbabwean flags to then Lieutenant General Vitalis Zvinavashe, who later became the first Commander Defence Forces (1993), and Air Marshal Perrance Shiri in 1992, and subsequently in the ZNA to then Lieutenant General Constantine Chiwenga in 1993.
The approval of the Defence Amendment Bill saw the setting up of a single command for the Defence Forces in 1993. Rtd General Vitalis Zvinavashe became the first commander of the Zimbabwe Defence Forces, with the commanders of both the Army and the Air Force falling under his command. Following his retirement in December 2003, General Constantine Chiwenga, was promoted and appointed Commander of the Zimbabwe Defence Forces. Lieutenant General P. V. Sibanda replaced him as Commander of the Army.[51]
The ZNA currently has an active duty strength of 30,000. The air force has about 5,000 men assigned. The Zimbabwe Republic Police (includes Police Support Unit, Paramilitary Police) is also part of the defence force of Zimbabwe and numbers 25,000.[52]
In 1999, the Government of Zimbabwe sent a sizeable military force into the Democratic Republic of Congo to support the government of President Laurent Kabila during the Second Congo War. Those forces were largely withdrawn in 2002.
Zimbabwe National Army[]
- Main article: Zimbabwe National Army

Flag of the Army of Zimbabwe
The Zimbabwe National Army or ZNA was created in 1980 from elements of the Rhodesian Army, integrated to a greater or lesser extent with combatants from the ZANLA and ZIPRA guerrilla movements (the armed wings of, respectively, ZANU and ZAPU).
Following majority rule in early 1980, British Army trainers oversaw the integration of guerrilla fighters into a battalion structure overlaid on the existing Rhodesian armed forces. For the first year a system was followed where the top-performing candidate became battalion commander. If he or she was from ZANLA, then his or her second-in-command was the top-performing ZIPRA candidate, and vice versa.[53] This ensured a balance between the two movements in the command structure. From early 1981 this system was abandoned in favour of political appointments, and ZANLA/ZANU fighters consequently quickly formed the majority of battalion commanders in the ZNA.
The ZNA was originally formed into four brigades, composed of a total of 29 battalions. The brigade support units were composed almost entirely of specialists of the former Rhodesian Army, while unintegrated battalions of the Rhodesian African Rifles were assigned to the 1st, 3rd and 4th Brigades. The notorious Fifth Brigade was formed in 1981 and disbanded in 1984 after allegations of brutality and murder during the Brigade's occupation of Matabeleland in what has become known as Gukurahundi (Shona: "the early rain which washes away the chaff before the spring rains").[54][55]
Economy[]
- Main article: Economy of Zimbabwe
Zimbabwean exports in 2006

Crop production in Zimbabwe has rapidly fallen
The government of Zimbabwe faces a variety of economic problems after having abandoned earlier efforts to develop a market-oriented economy. Problems include a shortage of foreign exchange, soaring inflation, and supply shortages. Zimbabwe's involvement from 1998 to 2002 in the war in the Democratic Republic of the Congo drained hundreds of millions of dollars from the economy.[56]
Mineral exports, agriculture, and tourism are the main foreign currency earners of Zimbabwe.[57] Zimbabwe is the biggest trading partner of South Africa on the continent.[58] The downward spiral of the economy has been attributed mainly to mismanagement and corruption of the Mugabe regime and the eviction of more than 4,000 white farmers in the controversial land redistribution of 2000.[59][60][61][62] Since this land redistribution began, agricultural exports, especially tobacco, have declined sharply. The Zimbabwe Conservation Task Force released a report in June 2007, estimating 60% of Zimbabwe's wildlife has died since 2000. The report warns that the loss of life combined with widespread deforestation is potentially disastrous for the tourist industry.[63]
Inflation rose from an annual rate of 32% in 1998 to an official estimated high of 100,580.2% in January 2008,[64] a state of hyperinflation. Local residents have largely resorted to buying essentials from neighbouring Botswana, South Africa and Zambia. IMF economists estimated inflation at about 150,000% in Dec 2007.
In 2005, the government, led by central bank governor Gideon Gono, started making overtures that white farmers could come back. There were 400 to 500 still left in the country, but much of the land that had been confiscated was no longer productive.[65] In January 2007, the government even let some white farmers sign long term leases.[66] But, the government reversed course again and started demanding that all remaining white farmers leave the country or face jail.[67][68]
In August 2006, a new revalued Zimbabwean dollar was introduced, equal to 1000 of the prior Zimbabwean. The exchange rate fell from 24 old Zimbabwean dollars per U.S. dollar (USD) in 1998 to 250,000 prior or 250 new Zimbabwean dollars per USD at the official rate,[69] and an estimated 120,000,000 old or 120,000 revalued Zimbabwean dollars per US dollar on the parallel market,[70] in June 2007.
On June 21, 2007, the U.S. ambassador to Zimbabwe, Christopher Dell, told The Guardian newspaper that inflation could reach 1.5 million per cent (1,500,000%) by the end of the year. The current official inflation rate is above 26,000%[71] and the black-market exchange rate is Z$3,650,000 to the pound.[72][73] On July 13, 2007, the Zimbabwe government said it had temporarily stopped publishing (official) inflation figures, a move that observers said was meant to draw attention away from runaway inflation which has come to symbolize the country's unprecedented economic meltdown.[74]
Mugabe points to foreign governments and alleged "sabotage" as the cause of the fall of the Zimbabwean economy, as well as the country's 80% formal unemployment rate.[75] Critics of Mugabe's administration, including the majority of the international community, blame Mugabe's controversial programme which sought to seize land from white commercial farmers. Mugabe has repeatedly blamed sanctions imposed on Zimbabwe by the European Union and the United States for the state of the Zimbabwean economy. According to the United States, however, these sanctions target only seven specific businesses owned or controlled by government officials and not ordinary citizens.[76] During a meeting of the Southern African Development Community in 2007, a call was issued for the sanctions to be removed.[77] It should be noted that Rhodesia had a successful export-led economy despite harsh sanctions applied to the whole nation by the UK and other world powers.Template:Facts
[]
President Robert Mugabe of Zimbawe (also known as ZIM) ![]() , vowed in 2011 that his party would not back down from its controversial drive to force foreign-owned companies to sell majority shareholdings to local blacks.
, vowed in 2011 that his party would not back down from its controversial drive to force foreign-owned companies to sell majority shareholdings to local blacks.
Mugabe said his Zanu-PF party regarded black economic empowerment as a key part of the national liberation struggle, dismissing fears it would hurt economic recovery. "So we are saying we must take over our country and those partners, those outsiders, who want to work with us must do so as junior partners. We are the senior partners, no more the junior partners," he said.
Mugabe has said previously Zanu-PF will nationalise firms from countries that have imposed sanctions on Zimbabwe (also known as ZIM) ![]() , arguing they cannot operate freely while Western powers punish his party over charges of rights abuses.
, arguing they cannot operate freely while Western powers punish his party over charges of rights abuses.
These threats have to foreign investors in the resource-rich country, which has introduced a law specifying 51% of firms worth over $500,000 should be owned by black Zimbabweans under a five-year programme. 'Britain and America, this is our country and we have a right over its resources and we are taking control now'," Mugabe said.
Mugabe has seized and distributed white-owned commercial farms to landless blacks under the banner of correcting colonial injustices - said it was futile to appease "imperialist" Western powers.
Gaddafi was a former political ally to Mugabe.
A unity government with rival Prime Minister Morgan Tsvangirai's Movement for Democratic Change in 2009 has tried to ease a severe economic crisis blamed on policies.
The Zimbawe (also known as ZIM) ![]() economy has been devastated by hyperinflation as of 2010 and 2011.
economy has been devastated by hyperinflation as of 2010 and 2011.
Mugabe was 87 in 2011, and has been in power since independence from Britain in 1980.
Demographics[]
- Main article: Demographics of Zimbabwe
Zimbabweans of all races line up to cast their vote in the 2005 general election
According to the United Nations World Health Organization, the life expectancy for men is 37 years and the life expectancy for women is 34 years of age, the lowest in the world in 2006.[78] An association of doctors in Zimbabwe have made calls for President Mugabe to make moves to assist the ailing health service.[79] Zimbabwe has a very high HIV infection rate. In 2006, the HIV rate was estimated to be 20.1% for people aged 15–49.[80] UNESCO reported a decline in HIV prevalence among pregnant women from 26% in 2002 to 21% in 2004.[81] Zimbabwe's total population is 12 million.[82]
English is the official language of Zimbabwe, though less than 2.5%, mainly the white and Coloured (mixed race) minorities, consider it their native language. The rest of the population speak Shona (76%) and Ndebele (18%).[83] Shona has a rich oral tradition, which was incorporated into the first Shona novel, Feso by Solomon Mutswairo, published in 1956.[84] English is spoken primarily in the cities, but less so in rural areas. Radio and television news is now broadcast in English, Ndebele, and Shona.
Sixty two percent of Zimbabweans attend Christian churches.[85] The largest Christian churches are Anglican, Roman Catholic, Seventh-day Adventist[86] and Methodist. However like most former European colonies, Christianity is often mixed with enduring traditional beliefs. Besides Christianity, ancestral worship is the most practiced non-Christian religion which involves ancestor worship and spiritual intercession; the Mbira Dza Vadzimu, which means "Voice of the Ancestors", an instrument related to many lamellophones ubiquitous throughout Africa, is central to many ceremonial proceedings. Mwari simply means "God the Creator" (musika vanhu in Shona). Around 1% of the population is Muslim.[87]
Black ethnic groups make up 98% of the population. The majority people, the Shona, comprise 80 to 84%. The Ndebele are the second most populous with 10 to 15% of the population.[88][89] The Ndebele are descended from Zulu migrations in the nineteenth century and the other tribes with which they intermarried. Support for the opposition is particularly strong both from the Ndebele and the Shona majority. Up to one million Ndebele may have left the country over the last five years, mainly for South Africa. Bantus of other ethnicities are the third largest with 2 to 5%.[89]
Other less populous Zimbabwean ethnic groups include white Zimbabweans, mostly of British origin, but some are of Afrikaner, Portuguese and Dutch origin as well, who make up less than 1.0%. The white population dropped from a peak of around 296,000 in 1975 to possibly 120,000 in 1999, and was estimated at no more than 50,000 in 2002, possibly much less.[90] Most emigration has been to the UK, South Africa, Botswana, Zambia, Australia and New Zealand. Mixed race citizens are 0.5% and various Asian ethnic groups, mostly of Indian and Chinese origin, are also 0.5%.[91] Asian immigrants are influential in the economic sector.
Refugee crisis[]
The economic meltdown and repressive political measures in Zimbabwe have led to a flood of refugees into neighbouring countries. An estimated 3.4 million Zimbabweans, a quarter of the population, had fled abroad by mid 2007.[92] Some 3 million of these have gone to South Africa.[93]
Apart from the people who fled into the neighbouring countries, an estimated 570,000 people are displaced within the borders of the country, many of whom remain in transit camps and have limited access to assistance. Most of the displaced have been victims of the Operation Murambatsvina in the year 2005 and continuing evictions and violent farm seizures. Their plight is virtually impossible to assess, as there has been no national survey of people displaced since 2005.[94]
However, these numbers are likely to have been exaggerated, as a study by the Forced Migration Studies Program of Witwatersrand University finds. [95]
Education[]
- Main article: Education in Zimbabwe

Zimbabwe's adult literacy rate is amongst the highest in Africa
Zimbabwe has an adult literacy rate of approximately 90% which is amongst the highest in Africa.[96][97][98] However, since 1995 the adult literacy rate of Zimbabwe has steadily decreased which is a trend shared by other African countries.[99]
The majority of the wealthier portion of the population send their children to independent schools as opposed to the government-run schools which are attended by the poorer members of the black population as these have lower fee scales. School education was made free in 1980, but since 1988, the government has steadily increased the charges attached to school enrollment until they now greatly exceed the real value of fees in 1980. The Ministry of Education of Zimbabwe maintains and operates the government schools but the fees charged by independent schools are regulated by the cabinet of Zimbabwe.
Zimbabwe's education system consists of 7 years of primary and 6 years of secondary schooling before students can enter university in country or abroad. The academic year in Zimbabwe runs from January to December, with three month terms, broken up by one month holidays, with a total of 40 weeks of school per year. National examinations are written during the third term in November, with "O" level and "A" level subjects also offered in June.[100]
There are seven public universities as well as four church-related universities in Zimbabwe that are fully internationally accredited.[100] The University of Zimbabwe, the first and largest, was built in 1952 and is located in the Harare suburb of Mount Pleasant. Notable alumni from Zimbabwean universities include Welshman Ncube; Peter Moyo (of Amabhubesi); Tendai Biti, Secretary-General for the MDC; Chenjerai Hove, Zimbabwean poet, novelist and essayist; and Arthur Mutambara, President of one faction of the MDC. Many of the current politicians in the government of Zimbabwe have obtained degrees from universities in America or other universities abroad.
The highest professional board for accountants is the Institute of Chartered Accountants in Zimbabwe (ICAZ) with direct relationships with similar bodies in South Africa, Canada, UK and Australia. A qualified Chartered Accountant from Zimbabwe is also a member of similar bodies in these countries after writing a conversion paper. In addition, Zimbabwean-trained doctors only require one year of residence to be fully-licensed doctors in the United States. The Zimbabwe Institution of Engineers (ZIE) is the highest professional board for engineers.
However, education in Zimbabwe became under threat since the economic changes in 2000 with teachers going on strike because of low pay, students unable to concentrate because of hunger and the price of uniforms soaring making this standard a luxury.[101]
Culture and recreation[]
- Main article: Culture of Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe womens' field hockey teams receive gold medals at the 1980 Olympics
A Zimbabwe market place and bus terminus
Zimbabwe celebrates its independence on April 18, 1980.[102] Celebrations are held at the National Sports Stadium in Harare where the first independence celebrations were held in 1980. At these celebrations doves are released to symbolise peace and fighter jets fly over and the national anthem is sung. The flame of independence is lit by the president after parades by the presidential family and members of the armed forces of Zimbabwe. The president also gives a speech to the people of Zimbabwe which is televised for those unable to attend the stadium.[103]
Football and cricket are the most popular sports in Zimbabwe. The citizens of Zimbabwe have won four medals in the Olympic Games, one in field hockey at the 1980 Summer games in Moscow, and three in swimming at the 2004 Summer games in Athens.
Zimbabwe has also done well in the Commonwealth Games and All-Africa Games in swimming with Kirsty Coventry obtaining 11 gold medals in the different competitions.[104][105][106][107] Zimbabwe has also competed at Wimbledon and the Davis Cup in tennis, most notably with the Black Family, which comprises Wayne Black, Byron Black and Cara Black.
Traditional arts in Zimbabwe include pottery, basketry, textiles, jewelry, and carving. Among the distinctive qualities are symmetrically patterned woven baskets and stools carved out of a single piece of wood. Shona sculpture has become world famous in recent years having first emerged in the 1940s. Most subjects of carved figures of stylised birds and human figures among others are made with sedimentary rocks such as soapstone, as well as harder igneous rocks such as serpentine and the rare stone verdite. Shona sculpture in essence has been a fusion of African folklore with European influences. Internationally famous artists include Henry Mudzengerere and Nicolas Mukomeranwa. A recurring theme in Zimbabwean art is the metamorphosis of man into beast.[108] Zimbabwean musicians like Thomas Mapfumo, Oliver Mutukudzi, the Bhundu Boys and Audius Mtawarira have achieved international recognition.
Several authors are well known within Zimbabwe and abroad. Charles Mungoshi is renowned in Zimbabwe for writing traditional stories in English and in Shona and his poems and books have sold well with both the black and white communities.[109] Catherine Buckle has achieved international recognition with her two books African Tears and Beyond Tears which tell of the ordeal she went through under the 2000 Land Reform.[110] Prime Minister of Rhodesia, the late Ian Smith, has also written two books — The Great Betrayal and Bitter Harvest. The book The House of Hunger by Dambudzo Marechera won an award in the UK in 1979 and the Nobel Prize-winning author Doris Lessing's first novel The Grass Is Singing is set in Rhodesia.
Food[]

Raw Boerewors
Like many other Africans, a majority of Zimbabweans depend on a few staple foods. "Mealie meal" (cornmeal) is used to prepare bota, a porridge made by mixing the cornmeal with water to produce a thick paste. This is usually flavoured with peanut butter, milk, butter, or, sometimes, jam.[111] Bota is usually eaten for breakfast. Cornmeal is also used to make sadza, which is usually eaten for dinner, and by many for lunch as well. Sadza is prepared similarly to bota. However, after the paste has been cooking for several minutes, more cornmeal is added to thicken the paste. This meal is usually served with greens, (spinach, collard greens), beans, and meat that has been stewed, grilled, or roasted. Sadza is also commonly eaten with curdled milk, commonly known as lacto (mukaka wakakora), or a small dried fish called kapenta (matemba). On special occasions, rice and chicken with cabbage salad is served as the main meal.
Graduations, weddings, and any other family gatherings will usually be celebrated with the killing of a goat or cow, which will be braaied (an Afrikaner form of barbecue) for the family.
Afrikaner recipes are popular though they are a small group (0.2%) within the white minority group. Meat, beef and to a lesser extent chicken are especially popular, though consumption has declined under the Mugabe regime due to falling incomes. Biltong, a type of jerky, is a popular snack, prepared by hanging bits of spiced raw meat to dry in the shade.[112] Boerewors (Template:Pronounced — "Boo-ruh-vorse") is served with sadza. It is a long sausage, often well-spiced, composed of beef rather than pork, and barbecued.
Birthplace of Scouting[]
It was in Matabeleland during the First Chimurenga that Baden-Powell, the Founder of Scouting, and Frederick Russell Burnham, the Father of Scouting, first met and began their life-long friendship. In mid-June 1896, during a scouting patrol in Matobo Hills, Burnham taught Baden-Powell woodcraft. Practiced by frontiersmen of the American Old West and indigenous peoples of North America, woodcraft was generally unknown to the British. However, Baden-Powell recognized that wars in Africa were changing markedly and the British Army needed to adapt; so during their joint scouting missions, Baden-Powell and Burnham discussed the concept of a broad training program in woodcraft for young men, rich in exploration, tracking, fieldcraft, and self-reliance. These skills eventually formed the basis of what is now called scoutcraft, the fundamentals of Scouting. Later, Baden-Powell wrote a number of books on the subject, and even started to train and make use of adolescent boys, most famously during the Siege of Mafeking, during the Second Boer War.[113][114]
Tourism[]
- Main article: Tourism in Zimbabwe
The logo of the Zimbabwe Tourism Authority showing the Victoria Falls and the Zimbabwe Bird found at Great Zimbabwe

Victoria Falls, the end of the upper Zambezi and beginning of the middle Zambezi
Since the Land Reform programme in 2000, tourism in Zimbabwe has steadily declined. After rising during the 1990s, (1.4 million tourists in 1999) industry figures described a 75% fall in visitors to Zimbabwe in 2000. By December, less than 20% of hotel rooms had been occupied.[115] This has had a huge impact on the Zimbabwean economy. Thousands of jobs have been lost in the industry due to companies closing down or simply being unable to pay staff wages due to the decreasing number of tourists.
Several airlines have also pulled out of Zimbabwe. Australia's Qantas, Germany's Lufthansa and Austrian Airlines were among the first to pull out and most recently British Airways suspended all direct flights to Harare.[115][116] The country's flagship airline Air Zimbabwe still flies to the United Kingdom.
Zimbabwe boasts several major tourist attractions. Victoria Falls on the Zambezi River, which are shared with Zambia, are located in the north west of Zimbabwe. Before the economic changes, much of the tourism for these locations came to the Zimbabwe side but now Zambia is the main beneficiary. The Victoria Falls National Park is also in this area and is one of the eight main National Parks in Zimbabwe,[117] largest of which is Hwange National Park.
The Eastern Highlands are a series of mountainous areas near the border with Mozambique. The highest peak in Zimbabwe, Mount Nyangani at 2,593 m (8,507 ft) is located here as well as the Bvumba Mountains and the Nyanga National Park. World's View is in these mountains and it is from here that places as far away as 60–70 km (37–43 mi) are visible and, on clear days, the town of Rusape can be seen.

Great Zimbabwe as featured on the defunct $50 note
Zimbabwe is unusual in Africa in that there are a number of ancient ruined cities built in a unique dry stone style. The most famous of these are the Great Zimbabwe ruins in Masvingo, which have survived from the Monomotapa Empire. Other ruins include Khami Ruins, Zimbabwe, Dhlo-Dhlo and Naletale, although none of these is as famous as Great Zimbabwe.
The Matobo Hills are an area of granite kopjes and wooded valleys commencing some 35 kilometres south of Bulawayo, southern Zimbabwe. The Hills were formed over 2000 million years ago with granite being forced to the surface, then being eroded to produce smooth "whaleback dwalas" and broken kopjes, strewn with boulders and interspersed with thickets of vegetation. Mzilikazi, founder of the Ndebele nation, gave the area its name, meaning 'Bald Heads'. They have become famous and a tourist attraction due to their ancient shapes and local wildlife. Cecil John Rhodes and other early white pioneers like Leander Starr Jameson are buried in these hills at a site named World's View.[118]
National symbols, insignia and anthems[]
The two main traditional symbols of Zimbabwe are the Zimbabwe Bird and the Balancing Rocks.
Other national symbols exist, but have varying degrees of official usage, such as the flame lily and the Sable Antelope.
Zimbabwe Bird[]
- Main article: Zimbabwe Bird
The stone-carved Zimbabwe Bird appears on the national flags and coats of arms of both Zimbabwe and Rhodesia, as well as on banknotes and coins (first on Rhodesian pound and then Rhodesian dollar). It probably represents the bateleur eagle.
The famous soapstone bird carvings stood on walls and monoliths of the ancient city of Great Zimbabwe built, it is believed, sometime between the 12th and 15th centuries by ancestors of the Shona. The ruins, which gave their name to modern Zimbabwe, cover some 1,800 acres (7.3 km²) and are the largest ancient stone construction in Zimbabwe.[119]
When the ruins of Great Zimbabwe were excavated by treasure-hunters in the late nineteenth century, five of the carved birds they discovered were taken to South Africa by Cecil Rhodes. Four of the statues were returned to Zimbabwe by the South African government at independence, while the fifth remains at Groote Schuur, Rhodes' former home in Cape Town.
Balancing Rocks[]
- Main article: Balancing Rocks
Balancing Rocks are geological formations all over Zimbabwe. They are rocks perfectly balanced without other supports caused by the erosion of softer rock around an ancient granite intrusion that gets left exposed. They are often remarked on and have been depicted on both the paper money of the Zimbabwean dollar and the paper money of the Rhodesian dollar. The ones found on the current notes of Zimbabwe, named the Banknote Rocks, are located in Epworth, approximately 15 km (9.3 mi) south-east of Harare.[120] There are, however, many different formations of the rocks, incorporating single and paired columns of 3 or more rocks. These formations are a feature of south and east tropical Africa from northern South Africa northwards to Sudan. The most notable formations in Zimbabwe are located in the Matobo National Park in Matabeleland.
National anthem[]
"Blessed be the Land of Zimbabwe" (Template:Lang-sn;[1] Template:Lang-nd) is the national anthem of Zimbabwe. It was introduced in March 1994 after a nation-wide competition to replace "Template:Lang" as a distinctly Zimbabwean song. The winning entry was a song written by Professor Solomon Mutswairo and composed by Fred Changundega. It has been translated into all three of the main languages of Zimbabwe.
Zimbabwe[]
Background[]
External Links[]
- Wikipedia:Zimbabwe
- http://www.un.org/members/list.shtml
- http://www.olympic.org/uk/organisation/noc/index_uk.asp
Insights[]
Details[]
Languages[]
Simple Slogans[]
- Editor's Tips
- Hello =
- Thank you =
- News =
- Sports =
- Athlete =
Regional Slogans[]
- Editor's Tip
People[]
- Population in year =
Heros[]
Sporting Stars[]
- Kirsty Coventry, swimmer
Cultural Stars[]
- Celeb Figure -- replace name
A for Athlete[]
- Tips
Friends[]
Leads[]
Schools[]
Olympics[]
Beijing 2008 Olympics[]
Notes
Summary[]
Past Olympic Memories[]
Sport in Society[]
School sports[]
Physical Education[]
University sports[]
Fitness[]
Games[]
Play[]
Media[]
Newspapers[]
TV, video, cinema[]
Radio and Podcasts[]
Wikis[]
Blogs[]
Discussions, forums, newsgroups[]
Open Source[]
Places[]
Sporting sites[]
Urban[]
Rural[]
Nature[]
Communities, Villages[]
In the garden[]
Business[]
Wikinomics[]
- Editor tips
Buzz[]
- Tell us what's hot.
Brands[]
Global brands
Sports sponsors[]
Imports[]
Exports[]
Sweatshops[]
- Editors tips on sweatshops
Government[]
Diplomats and Embassy Notes[]
Friction[]
Rivals[]
- Test matches against foes are more intense.
History[]
Travel[]
Destinations[]
- Don't miss spaces:
Photos[]
Locals travel to:[]
Visitors from abroad often include:[]
Travel accounts[]
Music[]
Notes and pointers to tunes.
Dates[]
Holidays[]
Sporting Festivals[]
- ↑ [http://www.alertnet.org/thefacts/reliefresources/112239842449.htm Crisis profile: Zimbabwe's humanitarian situation(26 July, 2005) Reuters Foundation AlertNet
- ↑ Zimbabwe, History Department of UKZN.
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Chippindale, Christopher. Pictures in Place: Looking at Pictures in Place. Page 15.
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ So Who Was Shaka Zulu- Really? Africa Stage
- ↑ Hensman, Howard. Cecil Rhodes: A Study of a Career. Page 106–107.
- ↑ Parsons, Neil. A New History of Southern Africa, Second Edition, 1993. London: Macmillan. Pages 178–181.
- ↑ Bryce, James. Impressions of South Africa. Page 170.
- ↑ Gray, J. A. (1956). "A Country in Search of a Name." The Northern Rhodesia Journal III (1) (1956). Page 78.
- ↑ Palamarek, Ernie. Hatari. Page 132.
- ↑ Parsons (1993). Page 292.
- ↑ Judd, Denis. Empire: The British Imperial Experience from 1765 to the Present. Page 372.
- ↑ Parsons (1993). Pages 318–320.
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Zambia political background NationsEncyclopedia.com, 2003
- ↑ 1 June 1979 BBC News
- ↑ Chung, Fay. Re-living the Second Chimurenga: memories from the liberation struggle in Zimbabwe, Preben (INT) Kaarsholm. Page 242.
- ↑ Preston, Matthew. Ending Civil War: Rhodesia and Lebanon in Perspective. Page 25
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:PDFlink.
- ↑ Zimbabwe suspended indefinitely from Commonwealth, HumanRightsFirst.org, 8 December 2003
- ↑ Zimbabwe: Housing policy built on foundation of failures and lies, Amnesty International, 9 August 2006
- ↑ Crisis profile: Zimbabwe's humanitarian situation, July 26, 2005. AlertNet.
- ↑ "Zimbabwe Life Expectancy Lowest In The World", Public Health News, 10 April, 2006
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ 29.0 29.1 Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Constitution of Zimbabwe Amendment (No. 17) Act, 2005 NGO Network Alliance Project
- ↑ Mugabe, Robert. (2007). Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica 2007 Ultimate Reference Suite. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica.
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Zimbabwe: Election Fraud Report, University of Pennsylvania, 18 April 2005
- ↑ Zimbabwe stands 'on a precipice' BBC, 31 March 2008
- ↑ http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/africa/7467990.stm
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ "Zimbabwe’s MDC factions reunite", SABC News, April 28, 2008.
- ↑ 39.0 39.1 "Opposition reunites in Zimbabwe", BBC News, April 28, 2008.
- ↑ Cris Chinaka, "All eyes on Zim as ZEC wrap-up recount", Reuters (IOL), April 29, 2008.
- ↑ Mugabe's former ally accuses him of foul play, March 12, 2005. Independent Online Zimbabwe.
- ↑ 42.0 42.1 Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ 44.0 44.1 Template:Citation/make link. BBC. 2007-03-14. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/africa/6449691.stm. Retrieved 2007-12-02.
- ↑ 45.0 45.1 Template:Cite web
- ↑ ZIMBABWE Press, Media, TV, Radio, Newspapers Press Reference, 2006
- ↑ Zimbabwe newspaper bombed BBC News, 28 January 2001
- ↑ Zimbabwe: Newspaper Silenced, February 7, 2004. New York Times.
- ↑ Why did Zimbabwe ban the BBC?, April 1, 2005. BBC News.
- ↑ Al Jazeera kicked out of Zimbabwe, June 22, 2008. Zimbabwe Metro.
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedminist - ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite book
- ↑ Nyarota, Geoffrey. Against the Grain. Page 134.
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Organised Violence and Torture in Zimbabwe in 1999, 1999. Zimbabwe Human Rights NGO Forum.
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Citation/make link. Africa News. 2007-10-31. http://www.africanews.com/site/list_messages/12598. Retrieved 2007-12-03. "Zimbabwe remains South Africa's most important trading partner in Africa"
- ↑ "Zimbabwe President Mugabe labels white farmers 'enemies'" — CNN — April 18, 2000
- ↑ Robinson, Simon. "A Tale of Two Countries" — Time Magazine — Monday, Feb. 18, 2002
- ↑ "Zimbabwe forbids white farmers to harvest" — USA Today — 06/24/2002
- ↑ "White farmers under siege in Zimbabwe" — BBC — Thursday, 15 August, 2002
- ↑ Nick Wadhams (2007-08-01). Template:Citation/make link. Nairobi: National Geographic News. http://news.nationalgeographic.com/news/2007/08/070801-zimbabwe-animals.html. Retrieved 2007-08-05.
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Meldrum, Andrew. "As country heads for disaster, Zimbabwe calls for return of white farmers" — The Guardian — May 21, 2005
- ↑ Timberg, Craig. "White Farmers Given Leases In Zimbabwe" — Washington Post — Saturday, January 6, 2007
- ↑ "Zimbabwe threatens white farmers" — AP — (c/o Washington Post — Monday, February 5, 2007
- ↑ Chinaka, Cris. "Zimbabwe threatens white farmers on evictions" — Reuters — August 8, 2007
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ CIA World Factbook: Zimbabwe
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ US predicts regime change in Zimbabwe as hyperinflation destroys the economy The Guardian The Guardian.
- ↑ Harare suspends release of inflation data, The Zimbabwe Situation.
- ↑ How to stay alive when it all runs out, July 12, 2007. The Economist.
- ↑ Template:Cite press release
- ↑ Analysis: Africa fails again to deal with Zimbabwe, The Jerusalem Post, 1 April 2007
- ↑ Template:Cite book
- ↑ Peta Thornycroft (2006-04-10). Template:Citation/make link. Harare: Sydney Morning Herald. http://www.smh.com.au/news/world/in-zimbabwe-life-ends-before-40/2006/04/09/1144521210993.html. Retrieved 2006-04-10.
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Zimbabwe GAP Adventures
- ↑ Mother Tongue: Interviews with Musaemura B. Zimunya and Solomon Mutswairo University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ 89.0 89.1 Template:Cite web
- ↑ Quarterly Digest Of Statistics, Zimbabwe Printing and Stationary Office, 1999
- ↑ Quarterly Digest of Statistics, 1998, Zimbabwe Printing and Stationary Office
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ CIA World Factbook
- ↑ Botswana Literacy Survey 2003, Central Statistics Office, Botswana
- ↑ Template:PDFlink.
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ 100.0 100.1 Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite book
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Citeweb
- ↑ Template:Cite journal
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ 115.0 115.1 Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Template:Cite web
All items (14)







